Controlling Stem Cell Behavior
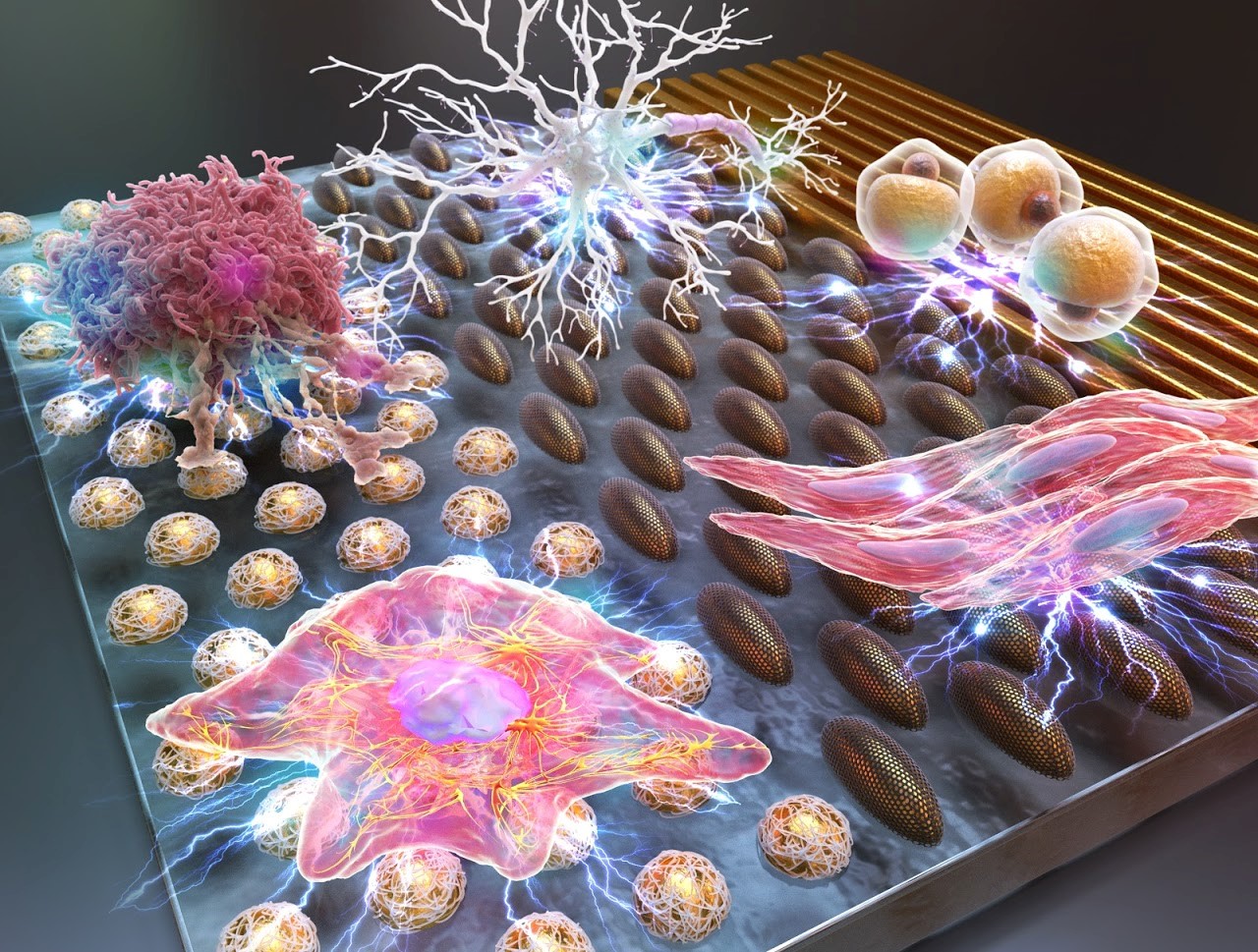
Stem cells have attracted increasing attention in the field of biomedicine and biomedical engineering because of their unique ability to differentiate into different cell lineages. A better understanding of the function of biomechanical cues (i.e. nano-topographical effect, surface functionality, stiffness, etc) on cell behavior can aide the development of a novel platform that utilizes the optimized biomechanical cues for guiding stem cell differentiation into specific cell lineages in an efficient manner. To realize the full potential of stem cells, a fundamental study that can elucidate the mechanisms of biomechanical cues on stem cell differentiation is needed to develop efficient biomechanical platforms for cell-based therapies and disease models.
Biosensor Development
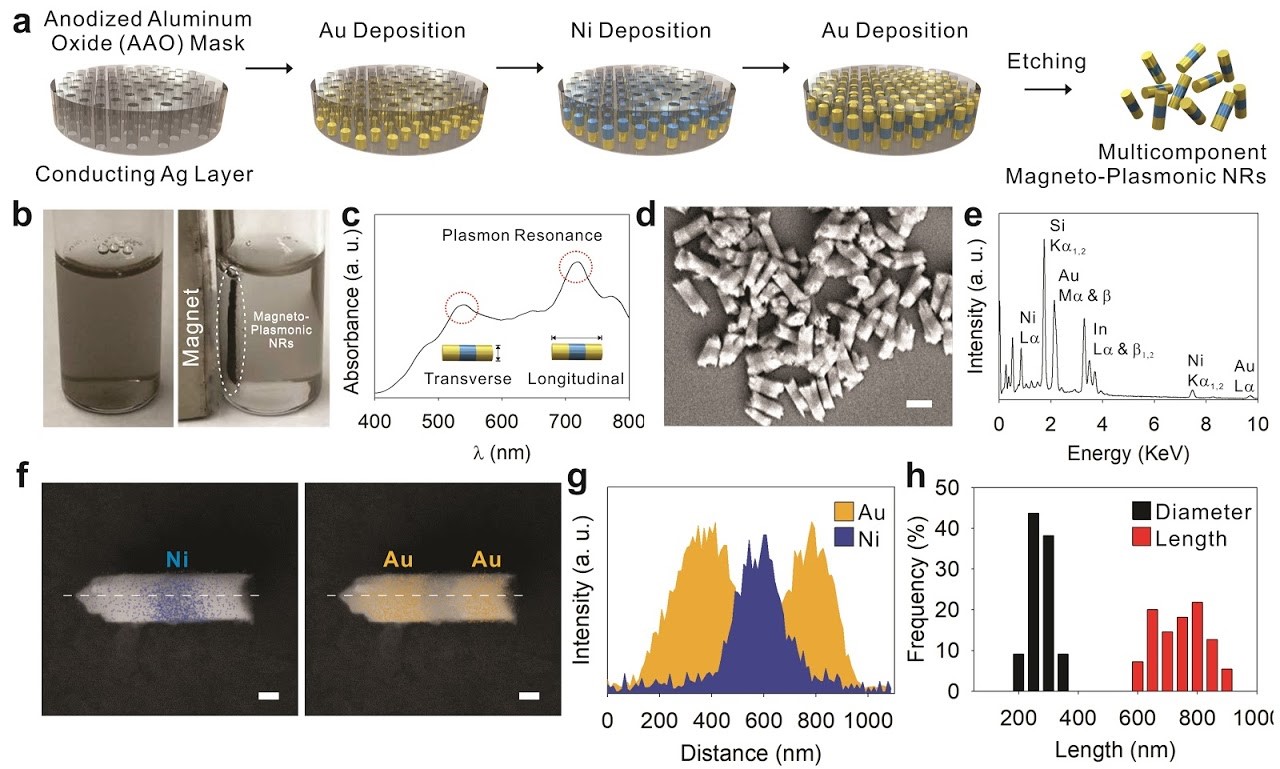
Single molecular detection of bio-molecule is important in clinical and environmental sensing fields. While many biosensor designs exist and are currently under active investigation and refinement, certain aspects are universal. At a fundamental level, biosensors must be able to recognize and record biological phenomena and transduce that event into an electrical signal for further data processing. Analyte recognition is especially significant with samples that undergo minimal processing and are prone to extraneous biomolecules that mask the signal from the intended analyte.
Nanomaterial Synthesis
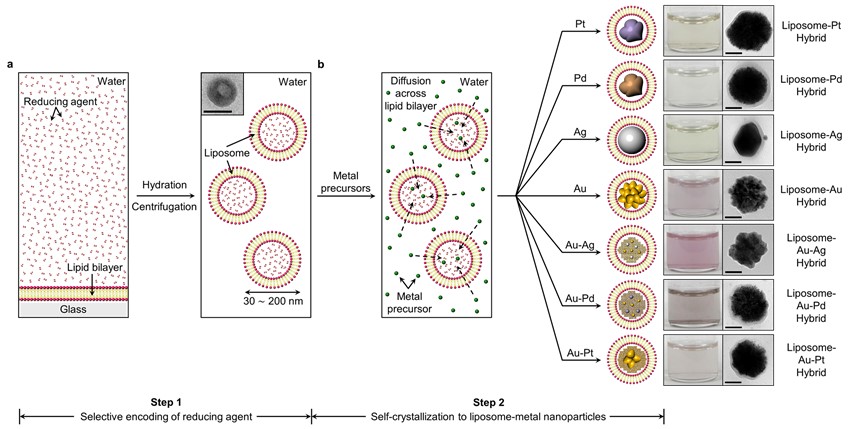
Inorganic nanoparticles have been extensively studied for a wide range of biomedicine due to their unique physical properties and appropriate size for labeling and probing biological systems. However, despite the significant investigation of nanoparticle for biomedical applications, their translation into clinical use still encounters considerable experimental difficulties. When nanoparticles are introduced to a complex biological environment containing bio-macromolecules (for example, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, etc.), they are often subjected to form aggregation and significantly alters in vivo behaviors with misrepresentative results (biodistribution, endocytosis efficiency, cytotoxicity, pharmacokinetics, etc). Hence, a novel reliable strategy for providing the hybrid structure with high stability and tunability of the inorganic part is highly desirable.
 JHLee Group -
JHLee Group -